SERVICE

By analyzing a portion of tissue from the miscarried fetus using next-generation sequencing (NGS), the genetic causes of miscarriage can be identified. This provides accurate information on the cause of miscarriage and offers genetic counseling to help prepare for the next pregnancy more quickly.
According to a study on chromosomal abnormality types and incidence rates in products of conception from natural miscarriages in Korea, the most frequently reported cause of miscarriage was fetal chromosomal aneuploidy.

Trisomy 16
Three copies of chromosome 16

Monosomy X
Single X chromosome
Trisomy 22
Three copies of chromosome 22
| Type of occurrence | Number of cases | Incidence rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Trisomy 16 | 34 | 13.3 |
| Monosomy X | 32 | 12.5 |
| Trisomy 22 | 23 | 9.0 |
| Trisomy 21 | 21 | 8.2 |
| Polyploidy | 21 | 8.2 |
| Trisomy 15 | 17 | 6.7 |
| Trisomy 18 | 9 | 3.5 |
| Trisomy 13 | 9 | 3.5 |
| Trisomy 9 | 8 | 3.1 |
| Others | ... | ... |
| Total | 255 | 100.0 |
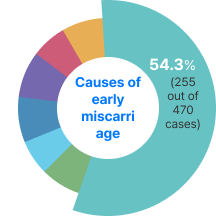
More than 80% of spontaneous miscarriages
occur within the first 12 weeks of pregnancy.
The majority are reported to be due to
fetal chromosomal abnormalities: 54.3% (255/470 cases).
Genetic factors
Immune factors
Endocrine factors
Anatomic factors
Lifestyle factors
Infections
Unknown causes
Han SH et al. J Genet Med. 2011.
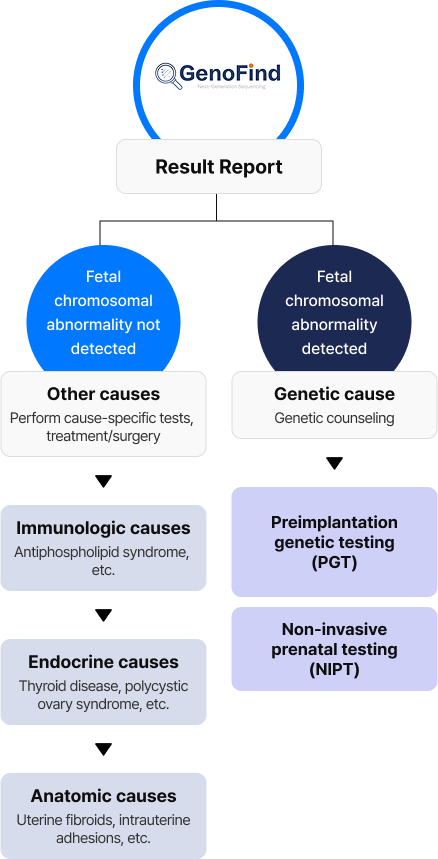
Karyotyping, which checks chromosomal structure through cell culture, often shows low detection rates for chromosomal abnormalities due to issues such as cell contamination, culture failure, and methodological limitations. As a result, the cause of miscarriage often cannot be identified.
1) 1. Cell contamination: overgrowth of maternal cells, bacterial or microbial contamination
2. Culture failure: failure of cell engraftment
3. Test limitations: high rate of inconclusive results due to culture failure
GenoFind, on the other hand, uses high-resolution next-generation sequencing (NGS) without cell culture to analyze the entire genome, providing a faster and more accurate method for detecting chromosomal aneuploidies.
| Test name | Karyotyping | NGS |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Karyotype analysis | Next-generation sequencing |
| Cell culture | O | X |
| Turnaround time | More than 3 weeks | Within 2 weeks |
| Sensitivity | Low | Very high |
| Analytical resolution | Low (Mb level) | High (bp level) |
 |
 |
“GenoFind is a test that analyzes the cause of miscarriage by detecting chromosomal aneuploidies in products of conception using NGS technology.”
Products of conception

Secure delivery by a certified courier service

Next-generation sequencing (NGS) analysis

Detection of chromosomal abnormalities in the miscarried fetus
| Test name | Chromosomal analysis of products of conception (POC) |
|---|---|
| Method | Next-generation sequencing (NGS) (NGS, Next Generation Sequencing) |
| Test items | Products of conception (POC) (POC, Products of Conception) |
| Specimen collection | Sterile container: 15 mL conical tube Sterile solution: 1 mL normal saline |
| Testing period | When tissue from the miscarried fetus can be separated |
| Turnaround time | Within 14 days (from the date of receipt) |

The company informs customers through the Privacy Policy about how the personal information provided is used and what measures are taken to protect personal information.
- Identifying individuals, verifying real names, confirming intent to sign up, and ensuring age-restricted service usage based on service use.
- Fulfilling contracts related to service provision, such as billing for services provided, delivering content, purchasing and processing payments, and dispatching items or billing statements.
- Delivering notices, ensuring communication for handling complaints, and ensuring accurate delivery information for item shipments.
- Providing information on new services and offering personalized services.
- Facilitating smooth provision of high-quality services.
- Name, company name, email, address, contact number, mobile phone number, inquiry details, and other optional items.
- As a general rule, personal information is destroyed immediately once the purpose for its collection or provision has been fulfilled.
- However, for the purpose of ensuring smooth service consultations, the content of the consultation may be retained for 3 months after completion. In cases where other laws, such as the Act on the Consumer Protection in Electronic Commerce, require preservation, the information may be retained for a specified period.
The company, as a general rule, destroys personal information without delay after the purpose of collection and use has been fulfilled. Information entered for membership or other purposes is transferred to a separate database (or, in the case of paper records, to a separate file) and stored for a certain period according to internal policies and relevant laws before being destroyed. Personal information transferred to a separate database is not used for any other purpose unless required by law. Personal information stored in electronic file formats is deleted using technical methods that prevent the recovery of the records.

The collection of email addresses posted on this website using email collection programs or other technical devices is prohibited, and violators may be punished under the Act on Promotion of Information and Communications Network Utilization and Information Protection.