SERVICE

By analyzing newborn cord blood or heel-prick blood using next-generation sequencing (NGS), this test screens for congenital chromosomal disorders such as intellectual disability, developmental delay, and autism spectrum disorders.
Early detection of newborn conditions allows timely treatment and intervention to help reduce or manage symptoms.
Newborn Screening Test
Many disorders caused by numerical or structural chromosomal abnormalities may not show visible symptoms at birth, making it easy to miss the critical window for treatment. The GenoBenet test enables the early detection of chromosomal disorders—including intellectual disability, developmental delay, autism, and ADHD—helping ensure timely treatment and ongoing care.

Intellectual disability

Developmental delay

Autism

ADHD
To determine whether a baby carries chromosomal abnormalities related to disease, the entire set of chromosomes must be analyzed—since abnormalities can occur at any location.
That’s why next-generation sequencing (NGS) is used: it can precisely detect deletions or duplications, even when they occur in small, specific regions across the genome.
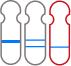
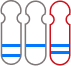
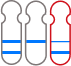
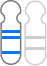
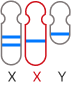
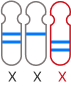
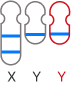
The GenoBenet test analyzes all 23 pairs of chromosomes for trisomy, monosomy, and deletion/duplication regions.
Deletion: loss of part of a chromosome
Duplication: duplication of part of a chromosome
※ Note
The selection of GenoBenet test items is based on rare disease codes listed in Orphanet, the European reference database for rare diseases.
Heel-prick blood or cord blood sample

Secure delivery by a certified courier service

Next-generation sequencing (NGS) analysis

Detection of congenital chromosomal disorders in newborns
| Test name | Newborn Genomic Screening Test (NBS) (NBS, Newborn Screening Test) |
|---|---|
| Method | Next-generation sequencing (NGS) (NGS, Next Generation Sequencing) |
| Test items | Detection of congenital chromosomal abnormalities that may occur across the entire genome |
| Testing period | From birth onward |
| Specimen information |
Heel-prick blood dried blood spot (minimum 2 spots) Cord blood ≥3 mL (EDTA tube, recommended) Whole blood ≥0.25 mL (EDTA tube) |
| Turnaround time | Within 14 days (from the date of receipt) |
If the GenoBenet test result is Detected, confirmatory testing (such as chromosomal microarray test) must be performed, and after final confirmation of the diagnostic result of the disease, genetic counseling is necessary.
If the GenoBenet test result is Detected, confirmatory testing (such as chromosomal microarray test) must be performed, and after final confirmation of the diagnostic result of the disease, genetic counseling is necessary.
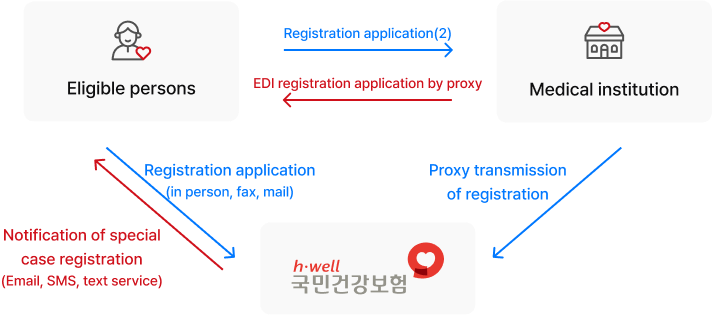
On the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency Rare Disease Helpline (https://helpline.kd-ca.go.kr/cdchelp/), you can access information on rare diseases. It provides details on symptoms, causes, specialized institutions, and statistical data for more than 1,300 rare diseases, as well as information on medical expense support programs and genetic testing support programs.
Medical expenses for more than 1,300 rare diseases are supported in Korea. After registering as a special case, both online application and offline application through public health centers are possible.
Proceed with confirmatory testing

Register as a special case beneficiary

Apply for the rare disease medical expense support program
The GenoBenet test report is provided as a premium booklet of approximately 40 pages.


The company informs customers through the Privacy Policy about how the personal information provided is used and what measures are taken to protect personal information.
- Identifying individuals, verifying real names, confirming intent to sign up, and ensuring age-restricted service usage based on service use.
- Fulfilling contracts related to service provision, such as billing for services provided, delivering content, purchasing and processing payments, and dispatching items or billing statements.
- Delivering notices, ensuring communication for handling complaints, and ensuring accurate delivery information for item shipments.
- Providing information on new services and offering personalized services.
- Facilitating smooth provision of high-quality services.
- Name, company name, email, address, contact number, mobile phone number, inquiry details, and other optional items.
- As a general rule, personal information is destroyed immediately once the purpose for its collection or provision has been fulfilled.
- However, for the purpose of ensuring smooth service consultations, the content of the consultation may be retained for 3 months after completion. In cases where other laws, such as the Act on the Consumer Protection in Electronic Commerce, require preservation, the information may be retained for a specified period.
The company, as a general rule, destroys personal information without delay after the purpose of collection and use has been fulfilled. Information entered for membership or other purposes is transferred to a separate database (or, in the case of paper records, to a separate file) and stored for a certain period according to internal policies and relevant laws before being destroyed. Personal information transferred to a separate database is not used for any other purpose unless required by law. Personal information stored in electronic file formats is deleted using technical methods that prevent the recovery of the records.

The collection of email addresses posted on this website using email collection programs or other technical devices is prohibited, and violators may be punished under the Act on Promotion of Information and Communications Network Utilization and Information Protection.